In life sciences organizations, Pharmacovigilance (PV) plays the role of a vigilant guardian, diligently monitoring patients’ safety and well-being. Combining drug safety and pharmacovigilance is essential for tracking medication safety after approval.
The International Data Corporation (IDC) reports that safety case volumes increase by 30-50% each year.
This upsurge can be attributed to multiple factors, including the introduction of an expanding array of new medications, heightened awareness among healthcare professionals and patients, the importance of drug safety and the complexity inherent in modern therapeutics, and the globalization of drug manufacturing.
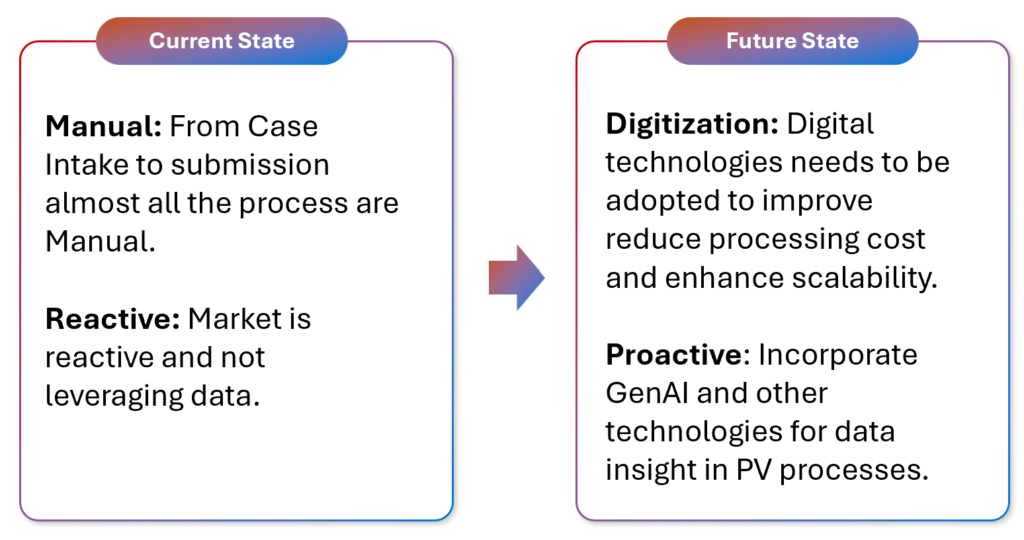
For these reasons, pharmaceutical companies are seeking to automate pharmacovigilance (PV) processes to speed the handling of adverse events, reduce costs, improve patient safety, and unlock opportunities alongside compliance. They want to move from reactive risk management to proactively predicting and preventing adverse events while automating mundane tasks such as data entry, triage, etc.
The Pharmacovigilance Process
The Pharmacovigilance process can be divided into five steps, starting with Case Intake.
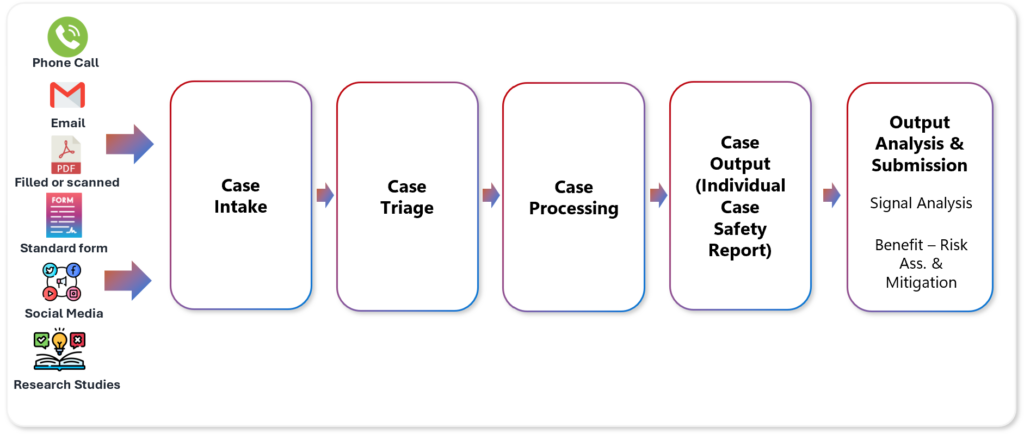
Case Intake: Most ADRs come from the FDA or a phone call. With rising awareness and access to digital tools, reporting from other channels, such as emails from Physicians with details or an attachment, online forms, and social media, is seeing a gradual spike. Learn more about PV Case Intake Process.
Case Triage: With the rising number of cases, it becomes imperative to filter noise for optimum resource utilization.
Case Processing: Processing includes coding the reported ADRs using standardized terminology (e.g., Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities—MedDRA) and ensuring data quality and completeness.
Case Output: Individual Case Safety Report (ICSR) is prepared with a description of the adverse event, a timeline of events, relevant medical history, concomitant medications, and any other pertinent information. This narrative provides additional context and aids in signal detection and assessment.
Submission, Risk, and Analysis: Case information is submitted to the pharmacovigilance database after review for further processing and analysis. This allows for systematic tracking, monitoring, and reporting of adverse events to regulatory authorities and other stakeholders as required by pharmacovigilance regulations.
Risk assessment evaluates adverse events’ severity, frequency, and impact, guiding decision-making on drug safety. Analysis involves thoroughly examining data to detect patterns and signals, aiding in identifying potential risks.
Cost Associated
According to the Everest Group 2019 study, companies spend an average of USD 420 – 425 per PV case. Considering an average inflation rate of 3% for the last four years, this figure becomes USD 458.
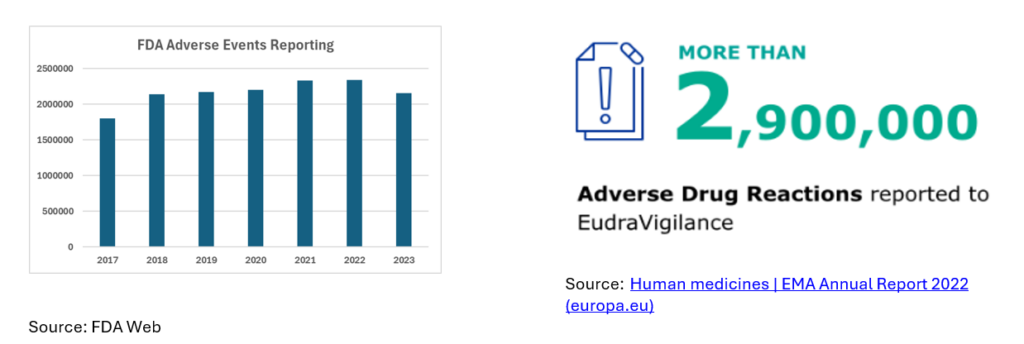
As per the FDA website (US market only), 2M cases were reported for 2023, leading to a spend of USD 1B on PV cases only, which is on the rise.
Europe registered 2,900,0001 ADRs, whereas MHRA from the UK mentioned 112,1282 ADRs in 2022.
Pharmacovigilance Future State
Stringent regulations, disruption in Supply Chain due to geopolitical reasons, margin pressure, improved customer awareness, and market competition are compelling pharmaceutical companies to revisit the way they operate pharmacovigilance cost centre.
Identifying Processes for Automation
The phase-wise approach has better acceptability, which allows the team to adjust to new technology and processes without impacting the business.
Data Capture
- Copilot can be introduced to streamline data capture, wherein the application can help users select from options. This will not only lead to completeness but also reduce errors.
- Optical Character Reading (OCR) can be used to read submitted PDF forms and scanned images, thus reducing time and error.
- Scanning Social Media—An NLP-based framework can help by creating meaningful insight from unstructured conversational data from social media sources like Twitter and Public Healthcare Forms (www.medications.com, www.healthboards.com) by identifying ADE and its relationship with drugs. This analysis can substantially reduce the company’s time to respond to market queries, thus maintaining their market reputation.
- OpenAI: For ‘Research Studies,’ Gen AI should be leveraged to scan documents and create a summary based on prompts.
Case Triage
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be leveraged to prioritize cases based on severity, such as hospitalization, life-threatening events, or death.
Case Processing and Output
- Advanced Analytics on existing data can become handy during case processing steps like checking for duplicates, medical coding using standardized (MEDRA) codes, and creating a Case Narrative in a standard format for review. With Natural Language Processing, ‘case narrative’ can be refined further.
Submission & Analysis
- Activities like Signal Analysis and Risk-benefit assessment require an appreciable understanding of drugs and associated diseases. ADR database, along with historical and recent studies, can be extracted and summarized using GenAI to develop models to help analyze signals and conduct risk-benefit assessments.
Benefits of Pharmacovigilance Automation
- Regulatory Compliance by submitting the case on time without errors.
- Reduce your Case Intake & triaging time by 40-50% of total time thus preparing the organization for scalability at reduced processing cost.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of artificial intelligence and automation on pharmacovigilance processes signifies a transformative shift towards intelligent PV. This evolution has far-reaching implications for drug development, commercialization, and the overall enhancement of drug safety and pharmacovigilance services.
References
- FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) Public Dashboard – FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) Public Dashboard | Sheet – Qlik Sense
- Human medicines | EMA Annual Report 2022 (europa.eu)
- Cognizant—Everest Group PEAK Matrix® for Pharmacovigilance and Complaint Management Services
- 1Europe: 2,900,000 Adverse Drug Reactions reported on EudraVigilance in 2022
- 2UK: As per MHRA, 112,128 Adverse Drug Reactions were reported in 2022