User engagement is crucial in today’s digital world. A good user experience (UX) attracts users and keeps them coming back, building loyalty and long-term value. This blog offers actionable UX strategies to boost engagement and create satisfying experiences.
Understanding User Engagement and Why It’s Crucial
User engagement is a key metric that determines the success of any digital product, service, or platform. It measures the extent to which users interact with and participate in a digital experience, such as a website, mobile app, or social media platform.
Key Aspects of User Engagement:
- Cognitive engagement: Users’ mental effort in a digital experience.
- Emotional engagement: Users’ emotional connection with a digital experience.
- Behavioral engagement: Users’ physical actions in a digital experience.
Metrics for Measuring User Engagement
- Time on page—The amount of time users spend on a particular page—or screen.
- Bounce rate—The percentage of users who leave a website—or app—immediately after arriving.
- Conversion rate—The percentage of users who complete a desired action—such as filling out a form, or making a purchase.
- Click-through rate (CTR)—The percentage of users who click on a link—or button.
- Session duration—The length of time users spend interacting with a digital experience.
- Return visits—The number of times users return to a digital experience.
Why User Engagement Matters
Engaged users contribute to the success of digital platforms in several ways:
- Increased conversions: Engaged users are more likely to convert, whether it’s making a purchase, filling out a form, or subscribing to a service.
- Improved customer loyalty: Users who are emotionally invested in a digital experience are more likely to return and recommend it to others.
- Enhanced user experience: Engaged users provide valuable feedback, helping to identify areas for improvement and inform design decisions.
How to Implement UX Strategies to Maximize User Engagement
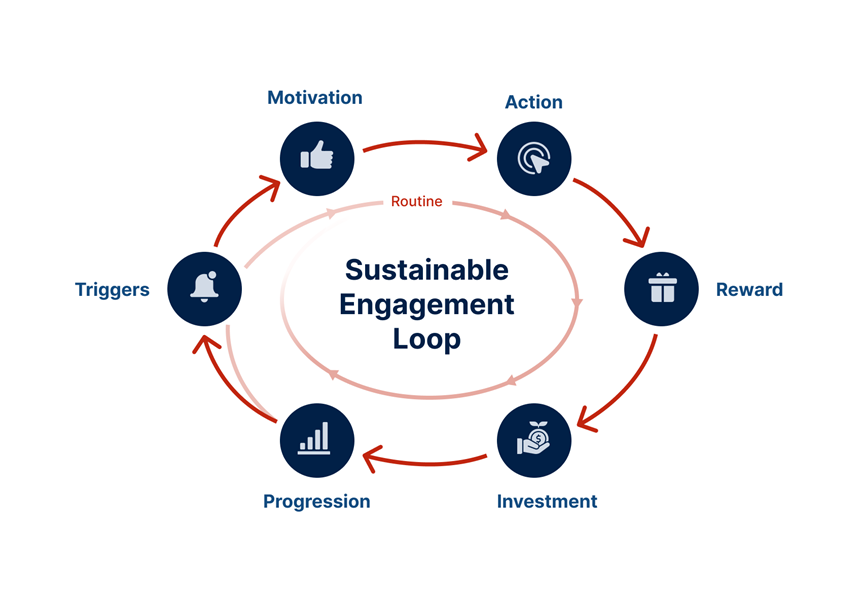
1. Creating Effective Triggers
A well-crafted trigger is the cornerstone of a successful engagement loop, making the difference between user action and disinterest.
- Ensure Timeliness and Balance Trigger Frequency – Triggers, such as notifications or prompts, must be timely and relevant. Overloading users with alerts can lead to fatigue, so striking the right balance is essential.
- Prioritize Personalized and Value-Driven Triggers – Customize triggers to match individual user preferences and ensure they provide clear value. Personalized triggers resonate more and boost user engagement.
- Leverage Internal Triggers Over Time – As users grow familiar with your product, they should develop internal triggers—habits that naturally lead them to engage with your product, reducing the need for external reminders. For instance, users might start checking a fitness app every morning without prompts.
2. Motivating Users to Engage
In behavioral design, motivation—and ability—are critical elements that ensure triggers lead to action. Two types of motivation drive user engagement—intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation springs from personal satisfaction or enjoyment, while extrinsic motivation relies on external rewards—such as points or reminders.
User ability can be broken down into several forms, including cognitive ability (mental effort), physical ability (ease of interaction), time availability (how much time users have), financial ability (the cost of taking action), and effort & skill (the knowledge or work required)—among other factors.
- Highlight the Reward (Cost-Benefit) – Clearly convey the benefits users gain by engaging with your product, such as saving time, achieving goals, or entertainment.
- Nudge Users to Make Small Early Commitments – Encourage users to start with small, low-effort actions. These initial commitments can lead to more significant, long-term engagement as users become familiar and trust the product.
- Balance Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation – Blend intrinsic rewards (like satisfaction or learning) with extrinsic incentives (such as discounts or recognition) to cater to a broader range of motivations.
3. Effortless and Nearly Instinctive Actions
Action is the core outcome of every carefully designed element. It’s not just about what users do; it’s about how easily they can perform that behavior.
- Design for Single-Task Focus – Remove distractions and direct users toward completing one task at a time. Simplified interfaces enhance decision-making speed and user satisfaction.
- Provide Instant Feedback – Offer immediate responses to user actions, like animations or confirmation messages, to show that their input is recognized and effective.
- Encourage Frequent Repetition of Routine Actions – Facilitate habitual behaviors by making routine tasks simple and rewarding, such as enabling one-click purchases or setting daily reminders.
4. Reinforce User Actions with Rewards
Rewards encourage users to engage with a product by offering immediate satisfaction or a sense of achievement.
Behavioral conditioning, from both psychology and animal training, shows how rewards shape and reinforce behaviors.
Fixed rewards give consistent reinforcement after a specific action, while variable rewards add surprise, engaging the brain’s dopamine system for stronger anticipation and engagement.
- Leverage the Power of Unpredictability – Introduce elements of surprise, such as unexpected rewards, to keep users engaged. This unpredictability taps into the psychology of anticipation.
- Gamify Experience with Points and Badges – Enhance the user experience through gamification. Points, badges, and leaderboards create a sense of accomplishment and encourage friendly competition.
- Create Social Rewards Through Competition or Recognition – Social validation is a strong motivator. Showcase user achievements in community settings or promote friendly challenges to foster peer recognition and engagement.
5. Investment Makes Users Less Likely to Abandon the Product
Driven by psychological mechanisms like the sunk cost fallacy. The more time, effort, or resources users invest in a product or platform, the more committed they become.
- Encourage Small Initial Investments and Content Contributions – Ask users for small commitments, like filling out a profile or uploading a photo. These actions increase their emotional investment in your product.
- Enable Personalization and Customization – Allow users to tailor their experience to suit their preferences, creating a sense of ownership and attachment.
- Create Opportunities for Long-Term Investment – Encourage users to build libraries, save preferences, or set long-term goals within your product to deepen their engagement over time.
6. Give Users a Sense of Growth and Accomplishment
Progression is the ongoing advancement a user experiences while interacting with a product, and milestones are key achievements that mark that progress. Unlike short-term rewards, which offer immediate gratification, progression and milestones provide long-term satisfaction, driving continued engagement.
- Display a Visible Progression Path – Use progress bars, achievement levels, or skill trackers to clearly indicate advancement, motivating users to keep engaging.
- Offer Tiered Milestones and Celebrate Them – Celebrate user milestones with personalized messages, badges, or rewards. These moments of recognition strengthen the user’s connection to your product.
- Incorporate Dynamic Difficulty Ramping – Adapt challenges to the user’s skill level, starting with easier tasks and gradually increasing difficulty to maintain interest and satisfaction.
Ethical Considerations for Designing Addictive Products
Ethical Considerations for Designing Addictive Products
While these strategies enhance engagement, ethical responsibility must be considered to prevent negative user behaviors, such as compulsive usage or excessive social validation.
- Avoid Doom-Scrolling and Limit Variable Reward Abuse – Design responsibly to prevent harmful behaviors like excessive scrolling. Set boundaries on variable rewards to foster a healthy user experience.
- Mitigate Social Validation Traps – Promote positive social interactions without exploiting users’ need for approval. Avoid features that prioritize engagement at the expense of user well-being.
- Provide Transparency and Algorithm Control – Provide users with insights into how your algorithms function and offer control over their experience, fostering trust and reducing dependency.
Using these UX strategies, designers can create engaging and sustainable products that offer lasting value and ensure a positive user experience.