In today’s fast-paced data landscape, organizations face the challenge of deriving actionable insights from growing data volumes with limited resources. This is where Copilot in Power BI becomes a huge differentiator by bringing in the power of Generative AI in supporting BI and visualization needs of customers. Copilot empowers analysts and business users to generate reports, analyze trends, and visualize data by simply describing their needs in natural language, thus reducing the need for extensive technical skills.
Copilot in Power BI
With the general availability (GA) of Copilot in Power BI, Microsoft Fabric takes a leap forward in simplifying data analytics. By integrating advanced generative AI, Copilot allows users to interact with data more naturally, providing a significant boost in productivity and collaboration across all levels of users.
Copilot for Microsoft Fabric is turned on by default in Fabric with an option to turn it off from the admin portal if an enterprise is not ready for it yet.
Key Features
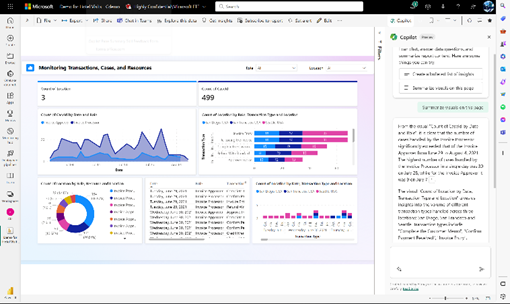
- Summarized Insights: Generate detailed insights and summaries in the Copilot pane from the dashboards and reports with natural language prompts, saving time for the analysts. This feature is not available for Power BI Desktop. Custom prompts help generate a nuanced summary to provide relevant, efficient, personalized answers with precision for improved decision making. Copilot also allows follow-up questions on summary.
Image source: Microsoft
- Natural Language Semantic Model Exploration (Preview): Allows users to describe datasets, semantic models for a quick understanding to build meaningful insights. Ask questions to Copilot for insights with visuals from your semantic model. At present Copilot cannot answer questions that require on-the-fly calculations or that need forecasting, anomaly detection or finding influencers. “Show reasoning” dropdown lets you learn how Copilot understands your questions.
- Report Authoring Features: From suggesting report topics to creating full narrative visuals, Copilot empowers users to build insightful reports faster with the following feature list.
- Suggest content for a visualization report
- Create a report page that can be further customized
- Create a summary visual on the report itself
- Ask Copilot questions about data in the model
- Add descriptions for your semantic model measures
- Add synonyms to enhance Q&A
Benefits of Copilot in Power BI for Business and IT
- Accessibility: Users without technical expertise can interact with data, query insights, and generate narratives intuitively.
- Productivity Gains: Speeds up insights by automating complex processes, allowing users to focus on decisionmaking.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces reliance on specialized data and visualization building teams, lowering operational costs.
- Faster Insights to Action: Automates report generation and data analysis, reducing the time needed for manual tasks.
- Data Democratization: Encourages a data-driven culture by enabling a wide range of users to leverage data insights.
Pre-requisites
- Minimum Fabric Capacity: F64 SKU (equivalent of erstwhile P1 of Power BI Premium capacity) is the minimum requirement to get the Copilot feature in Power BI.
- Copilot and Azure OpenAI Service: Turned on in Copilot Tenant Setting for specific security groups or for the entire organization. You can restrict copilot usage only based on security groups. But once enabled for a security group, it cannot be restricted based on workloads like Data Factory/Power BI/etc.
- Access criteria: At least “Read” access to the workspace to generate the summary from reports, and “Edit” access to create narrative visualizations and copilot reports in Power BI Service. For Power BI Desktop, you need admin, member or contributor access to at least one workspace that is Copilot-enabled. This need not be the same workspace where the reports are to be published.
It’s worthwhile to note that if your Fabric capacity lies outside of US and EU, then the administrator needs to enable setting for Copilot and Azure OpenAI services to be utilized by sending data outside your capacity’s geographic region, compliance boundary, or national cloud instance. However, even if the copilot GPU processing (consumption) zones are outside of the Fabric capacity’s billing region, the pricing according to the billing region is applicable.
Microsoft prioritizes region mapping for copilot consumption to Fabric billing based on data residency criteria of the same geographic area as much as feasible.
Pricing
- No separate license: Copilot in Microsoft Fabric doesn’t require a separate license. If you have any other Copilot licenses like for your Microsoft 365, or in-product licenses like Dynamic 365 – those will not work from within the workspace in Fabric.
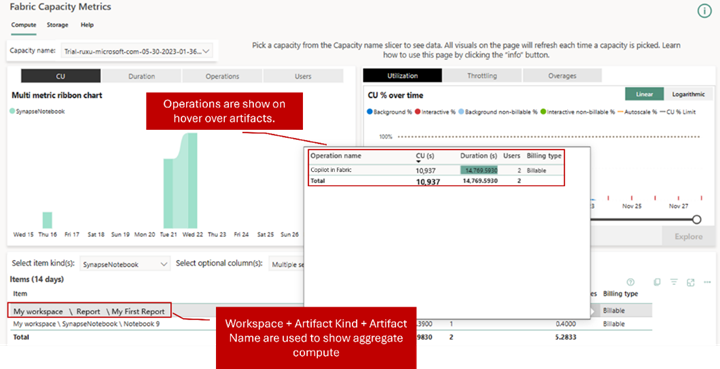
- No separate billing: The pricing for Copilot in Microsoft Fabric is baked in the SKU of Fabric capacity. The Copilot usage for Power BI report creation can be counted in terms of CU-seconds (Capacity Unit – seconds) for the input tokens supplied and output tokens generated. Check the capacity metrics for Power BI session service for usage details in “Copilot in Fabric” in your Fabric Capacity Metrics App.
- Easy to understand: The Copilot for the input to Power BI costs 400 capacity unit (CU)-seconds per 1000 input tokens. The output costs 1200 CU-seconds per 1000 output tokens. As an approximation, 1,000 tokens approximately translate to 750 words. The formula to arrive at overall capacity seconds:
Fabric Copilot in CU-seconds = (input token number x 400 + output token number x 1,200) / 1,000.
Image source: Announcing Copilot in Fabric pricing
Key Considerations
- How quickly can an enterprise experience throttling: Copilot in power BI needs F64 SKU that translates to 64×3600 = 230,400 CU-seconds per hour. Is that enough for a Power BI user-base of 1000? Remember, that co-pilot once enabled is enabled for all the workloads that it supports. Each user consuming 100 tokens on average for Copilot in Power BI at peak hour, can cause throttling for all the workloads for data ingestion, data engineering, data exploration and all even after ‘smoothing’ of interactive jobs over a period of 5 minutes and background jobs over a period of 24 hours as per the Fabric throttling policy.
- How accurate are the summaries: Copilot being an AI system, the accuracy of the response depends on several factors – how objective the prompts are, how descriptive the column names were in the semantic model, and many more. Reference footnote in the report summary allows the users to check the accuracy of the summary by showing which part of the visuals are referred to that part of the summary.
Expert guidance is needed to frame the policies and guardrails to avoid unwarranted behavior from Copilot and to ensure high accuracy of the outputs by building a solid data foundation along with linguistic modeling and a flexible design thinking approach to AI innovation.
Contact us today to learn how WinWire can help your AI-Copilot journey!