What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things is made up of three major parts: devices, communications, and computing. Devices are physical objects that are linked to the Internet. The second component is communication, which is carried out via Wi-Fi, satellites, and cellular services and is critical to the overall system’s operation. The third component is computation, which is performed centrally on the server and allows the system to run efficiently. An IoT application facilitates the integration of all three components for intelligent decision-making.
Why IoT is used?
We can use the internet of things to live and work more intelligently, as well as gain complete control over their lives. In addition to providing smart devices to automate homes, IoT is essential to business.
Companies can use IoT to automate processes and reduce labor costs. It also lowers the cost of manufacturing and delivering goods by reducing waste and improving service delivery. Like humans, each of your devices will learn from the experiences of other devices. The Internet of Things (IoT) aims to increase human interdependence by allowing people to interact, contribute, and collaborate with objects.
How IoT is used?
Sensor data is exchanged between IoT devices via a connection to an IoT gateway or other edge device, where it is either sent to the cloud for analysis or analyzed locally. These devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they receive.
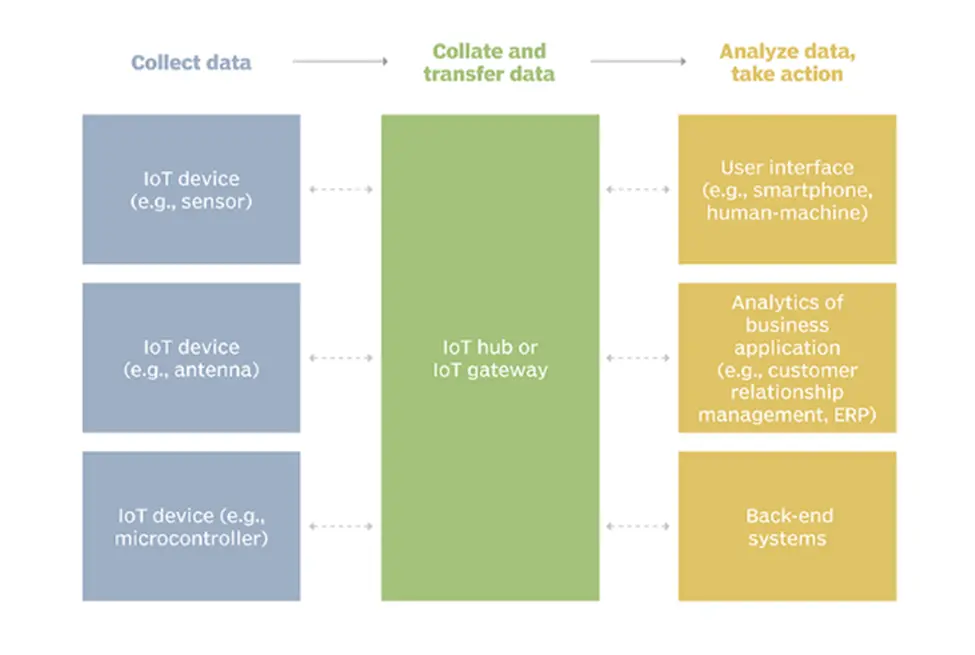
- Collection: In order to monitor the functioning of devices connected to the Internet of Things, sensors are used in IoT data collecting. The sensors gather and transmit real-time data that is saved and retrieved at any time in order to monitor the state of the IoT network.
Example: At our home, In the car, At the office, In the manufacturing plant
- Communicate: IoT is the linking of gadgets via the internet, allowing these intelligent objects to exchange data, execute some functions autonomously, and communicate with one another. These gadgets have electronics, software, networks, and sensors built in that facilitate connection.
Example: A cloud platform, Private data center, Home network
- Analyze: Analyzing data is about understanding what happened in the past. The first step in this stage is typically visualizing your historical IoT data on a dashboard. There’s an enormous amount of value in being able to see your information for the first time.
Analyzing data is also about processing information in different ways in order to derive insights from raw data.
Example: Visualizing the data, Building reports, Filtering data
- Action: Action defines what happens when a rule is triggered.
Example: Communicate with another machine (m2m), Send a notification (SMS, Text, Email), Talk to another system
IoT Testing
IoT app testing makes sure that every device effectively carries out all of its functions, enabling the entire IoT network to cooperate and execute as planned.
IoT testing is a subset of testing that examines IoT hardware. We should deliver better services more quickly. Global need for data access, production, consumption, and transmission is enormous. The goal is to provide insight and control over numerous linked devices.
Types of IoT Testing
- Usability testing: Usability testing is crucial for IoT testing because the users use a variety of devices for various measurements. As a result, opinions differ from user to user. Thorough usability testing should be done for the purposes of displaying data, processing data, etc.
- Compatibility testing: A software application’s ability to function properly across various browsers, databases, operating systems (OS), mobile devices, networks, and hardware is determined by a compatibility test.
- Data integrity Testing: In the IoT system, devices communicate with one another and share a lot of data. To check the data integrity of IoT systems, where the accuracy, format, compatibility, and sanctity of data are evaluated, is one of the processes involved in IoT testing. The information is verified using a variety of hardware, databases, gateways, and IoT servers.
- Security Testing: It is essential to evaluate every device in order to close security gaps and uphold the confidentiality and integrity of data. Data protection, device identity and authentication, data encryption and decryption, and cloud data storage are the main areas of attention in security testing.
- Performance Testing: Performance Testing in IoT is used to evaluate the IoT app’s overall performance and confirm the reaction time under various user loads, optimize the code to boost performance and test under various conditions like low battery, low memory, and switching between different networks.
IoT Testing Framework
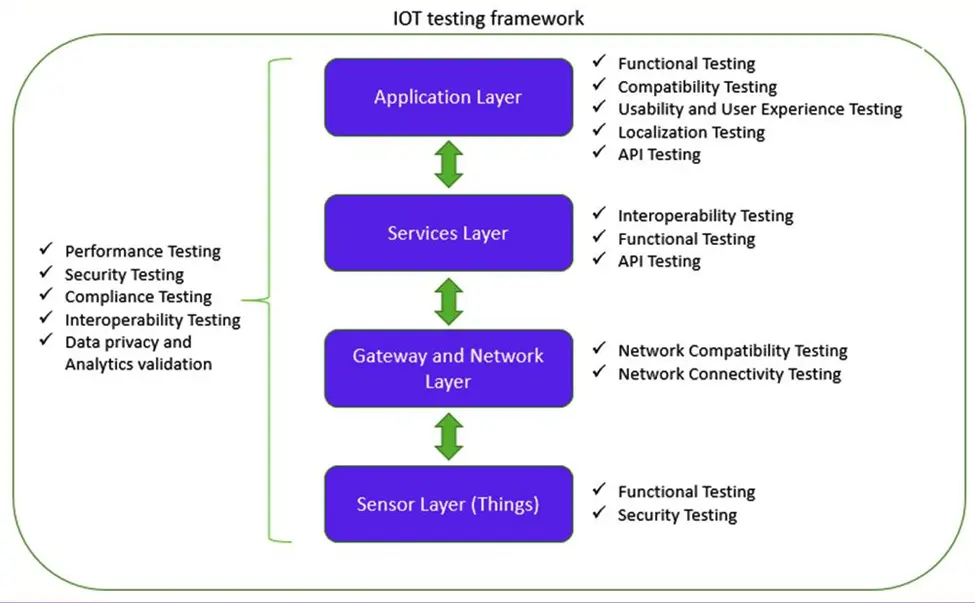
Testing for the Internet of Things requires a robust environment whose infrastructure depends on the devices involved in the IoT ecosystem. We can divide the IoT Testing Framework into the following levels:
- Application layer: Functional testing, compatibility testing, usability and user experience testing, API testing localization testing are performed at this level.
- Service layer: At this level, compatibility testing, functional testing, and API testing are performed.
- Gateway and network layer: It relates to network compatibility and network connectivity testing.
- Sensory layer: At this level, the tester will perform functional and security testing.
Challenges in IoT Testing
- Security and Privacy: IoT systems are extremely susceptible to cyberattacks. Since users believe the manufacturer has included security safeguards, they don’t take any action to protect their IoT devices. The device’s performance, operation, software updates, firmware upgrades, data encryption, data protection, and device password protection must all be examined.
- Network connectivity: Since the Internet of Things is all about transferring data at accelerating rates, network connectivity is essential. As a result, we need to test IoT architecture at different network speeds. We frequently use virtual network simulators to verify this by altering factors like network load, connectivity, and stability. But since real-time data and networks are always changing, the testing team is unsure of where the bottleneck will eventually form.
- Lack of knowledge and awareness: IoT is a new technology that few people are familiar with. Although most of the risks of IoT security issues are still on the manufacturing side, consumers and business procedures might still create more severe threats. The user’s ignorance and lack of understanding of IoT functioning is one of the main IoT security dangers and difficulties.
- Insufficient testing: Testing in a lab environment is insufficient for IoT devices since applications might fail adversely when exposed to real-time conditions and data but obtaining real time data for testing purposes becomes extremely difficult.
- Lack of standardization: Lack of standardization leads to a number of issues that impact interoperability, scalability, security, and communication. The lack of communication protocol standards can significantly affect the management of data from different devices.
Applications of IoT
- Smart Homes
- Smart City
- Self-driven Cars
- IoT Retail Shops
- Farming
- Wearables
- Smart Grids
- Industrial Internet
- Telehealth
- Smart Supply-chain Management
- Traffic management
- Water and Waste management
Technologies used:
- Radio Frequency Code (RFID)tags and Electronic Product Code (EPC)
- Near Field Communication (NFC) is used to activate two-way interaction between electronic devices.
- Bluetooth is used for short-range communication.
- Z-wave
- WIFI
IoT Testing Tools
- IoT Testing Tools for Software Testing: Wireshark, Tcpdump, Shodan, Thingful.
- IoT Testing Tools for Hardware Testing: JTAG Dongle, Digital Storage Oscilloscope, Software Defined Radio.
Conclusion
IoT can help innovate new processes and initiatives that could transform businesses, lives, and the world. People are also trying to understand what the many opportunities and challenges are going to be as more and more devices start to join the IoT. For now, the best thing that we can do is educate ourselves about what the IoT is and the potential impacts that can be seen on how we work and live.